Abstract
Background:
Imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib are standard frontline therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Although generally safe, they are associated with adverse events (AEs), each with a distinct toxicity profile. We conducted a meta-analysis of reported AEs to assess their toxicity profile at a larger scale.
Methods:
We searched reports from Pubmed/Medline, CENTRAL Cochrane registry, clinicaltrials.gov, and available final trial reports from pharmaceutical companies. We selected randomized phase 2 and 3 trials where imatinib, nilotinib and/or dasatinib were used and all-grade and grade 3-4 AEs were reported. We calculated the relative risk (RR), 95% confidence interval (95CI), and I2 statistic testing of heterogeneity.
Results:
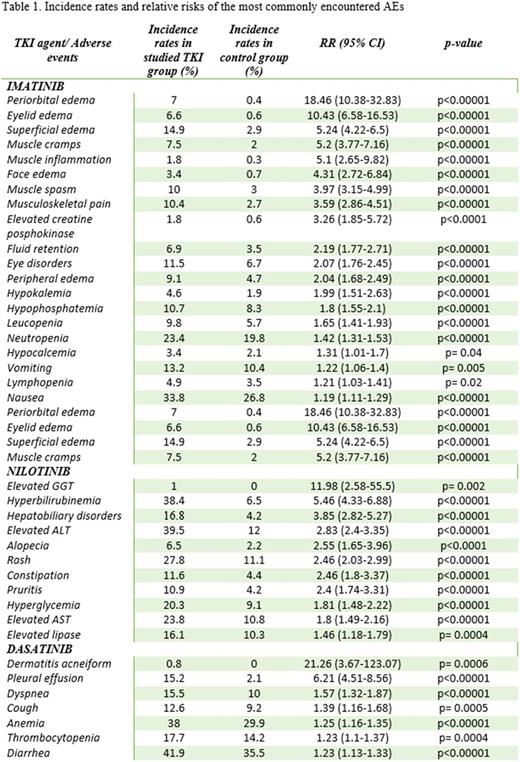
A total of 24 randomized clinical trials were included (11 phase 2, 13 phase 3) including 7491 pts treated for CML (15 studies), gastrointestinal stromal tumor (2), prostate cancer (3), breast cancer (2), pancreatic cancer (1), glioblastoma (1) and portal hypertension (1). (Table 1).
Imatinib had a high risk of fluid retention: RR of all-grade peripheral edema 2.04 (95CI 1.68-2.49); periorbital edema 18.46 (10.38-32.83); face edema 4.31 (2.72-6.84); eyelid edema 10.43 (6.58-16.53); superficial edema 5.24 (4.22-6.5), fluid retention 2.19 (1.77-2.71). Correlation with grade 3-4 of these events was not statistically significant.
Musculoskeletal AEs were also most common with imatinib: musculoskeletal pain, muscle spasm and elevated blood creatine phosphokinase had RR of 3.59 (2.86-4.51), 3.97 (3.15-4.99) and 3.26 (1.85-5.72). Muscle inflammation and muscle cramps were reported in 1 trial as 5.1 (2.65-9.82) and 5.2 (3.77-7.16). All-grade eye disorders in imatinib-treated patients had RR 2.07 (1.76-2.45).
Hepatobiliary disorders dominated in the nilotinib group with RR 3.85 (2.82-5.27), specifically: elevated AST, elevated ALT, elevated GGT and hyperbilirubinemia : 1.8 (1.49-2.16), 2.83 (2.4-3.35), 2.83 (2.4-3.35), 11.98 (2.58-55.5) and 5.46 (4.33-6.88).
Dasatinib-induced pleural effusion and associated symptoms were reported with RR of all-grade pleural effusion 6.21 (95CI: 4.51-8.56; p<0.00001); cough 1.39 (1.16-1.68; p=0.0005) and dyspnea 1.57(1.32-1.87; p<0.00001).
Hematological toxicities, all-grade leucopenia, neutropenia and lymphopenia were more pronounced with imatinib RR 1.65 (1.41-1.93), 1.42 (1.31-1.53) and 1.21 (1.03-1.41), respectively. Corresponding values for grade 3-4 were 1.81 (1.15-2.86), 1.39 (1.17-1.65) and 3.02 (1.24-7.38). There was higher RR of high-grade infections with imatinib 2.07 (1.44-2.97). Dasatinib was associated with higher risk of all-grade anemia and thrombocytopenia : 1.25 (1.16-1.35) and 1.23 (1.1-1.37).
For dermatological toxicities, nilotinib was associated with higher RR of all-grade rash, pruritis and alopecia : 2.46 (2.03-2.99), 2.4 (1.74-3.31) and 2.55 (1.65-3.96). Dasatinib was associated with dermatitis acneiform in 2 trials, RR 21.26 (3.67-123.07).
Gastrointestinal toxicities varied by drug. All-grade nausea and vomiting were more common with imatinib: 1.19 (1.11-1.29) and 1.22 (1.06-1.4); nilotinib correlated with all-grade constipation 2.46 (1.8-3.37); and all-grade diarrhea with dasatinib 1.23 (1.13-1.33).
Metabolic/electrolyte disturbances with imatinibincluded all-grade hypophosphatemia, hypocalcemia and hypokalemia : 1.8 (1.55-2.1), 1.31 (1.01-1.7) and 1.99 (1.51-2.63), and grade 3-4 hypophosphatemia 3.15 (2.28-4.36). Nilotinib had higher RR of hyperglycemia and elevated lipase 1.81 (1.48-2.22) and 1.46 (1.18-1.79).
Conclusion:
Our meta-analysis further demonstrates the different toxicity profile of different TKIs across several trials and different diseases. This information may be useful when selecting therapy for patients in need of a TKI.
Kantarjian: Novartis: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding. Jabbour: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Cortes: Sun Pharma: Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.